- Fayol has explained this principle with the help of a ladder. For example, in a company the employee ‘F’ wants to have contact with the employee ‘P’. According to the principle of scalar chain ‘F’ shall have to reach ‘A’ through the medium of E,D,C,B and then having contact with L,M,N,0 shall reach ‘P’.
- 14 Principles of HENRI FAYOL project on KFC Class-XII Slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance, and to provide you with relevant advertising. If you continue browsing the site, you agree to the use of cookies on this website.
- It is one of the principles of Henri Fayol. Management should promote a team spirit of unity and harmony among employees, according to Fayol. Tested in Laboratories Explanation: Principles of mangement cannot be tested in laboratories as these principles are applied on human behaviour.
Henri Fayol (1841-1925)

The functions go hand- in- hand with the Principles. Fayol’s practical list of principles guided early 2. 4 Principles of Management had a significant influence on present management theory. The list of principles is among the earliest theories of management and it.

Henri Fayol contributed much to early principles of management theory and is also considered a founding father of modern project management. The tools we have today as managers have roots in or were at least influenced by the works of the men we have been looking over so far. Fayol’s “14 principles of management” were released in almost one hundred years ago, 1914, but are still relevant today, as are his “six primary functions of management” – the core today of project management.
Fayol was born in Istanbul and began working as an engineer at a large mining company in France when he was 19, eventually becoming the director. In the following years he developed what he called the 14 most important principles of management, explaining how managers should organise and handle workers.
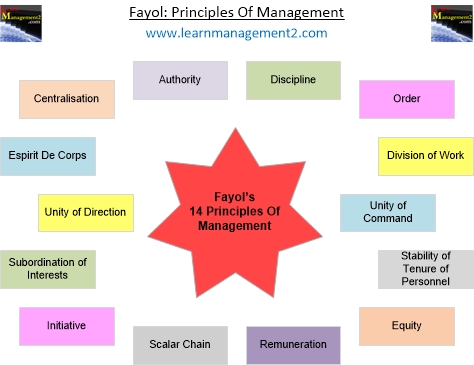
Fayol’s principles are listed below:
- Division of Work – when employees are specialised, output can increase because they become increasingly skilled and efficient.
- Authority – managers must have the authority to give orders, but they must also keep in mind that with authority comes responsibility.
- Discipline – discipline must be upheld in organisations, but methods for doing so can vary.
- Unity of Command – employees should have only one direct supervisor.
- Unity of Direction – teams with the same objective should be working under the direction of one manager, using one plan. This will ensure that action is properly coordinated.
- Subordination of Individual Interests to the General Interest – the interests of one employee should not be allowed to become more important than those of the group. This includes managers.
- Remuneration – employee satisfaction depends on fair remuneration for everyone. This includes financial and non-financial compensation.
- Centralisation – this principle refers to how close employees are to the decision-making process. It is important to aim for an appropriate balance.
- Scalar Chain – employees should be aware of where they stand in the organisation’s hierarchy, or chain of command.
- Order – the workplace facilities must be clean, tidy and safe for employees. Everything should have its place.
- Equity – managers should be fair to staff at all times, both maintaining discipline as necessary and acting with kindness where appropriate.
- Stability of Tenure of Personnel – managers should strive to minimise employee turnover. Personnel planning should be a priority.
- Initiative – employees should be given the necessary level of freedom to create and carry out plans.
- Esprit de Corps – organisations should strive to promote team spirit and unity.
Fayol’s “six primary functions of management”, which go hand in hand with the “Principles”, are as follows:
- Forecasting.
- Planning.
- Organising.
- Commanding.
- Coordinating.
- Controlling
Henri Fayol’s “14 Principles of Management” have been a significant influence on modern management theory. His practical list of principles helped early 20th century managers learn how to organise and interact with their employees in a productive way.
Although the 14 Principles aren’t widely used today, they can still offer guidance for today’s managers. Many of the principles are now considered to be common sense, but at the time they were revolutionary concepts for organisational management.
Fayol’s Principles of Management – Introduction
Fayol’s principles of management provide an important link in evolution of classical school of management thought. His contribution must be interpreted in terms of impact that his writings have improved managerial efficiencies.
Henri Fayol
Henri Fayol ( 29 July 1841 – 19 November 1925 ) was a French management theorist. He was a French mining engineer, and developed general theory of business administration that is called Fayolism.
Fayol’s work became famous with the 1949 publication of “General and industrial administration”, the English translation of the 1916 article “Administration industrielle et générale”. Fayol had also written several articles on mining engineering, starting in the 1870s, and some research papers on administration.
He is also regarded as ‘Father of General Management’. The 14 principles given by Fayol act as a combined solution for the managers to apply in their business practices.
Principles of Management are statements, based on fundamental truths. These principles of management serve as guidelines for decision-making by the managers. They are formed based on observation by experts and practice done by them. Henri Fayol was able to frame 14 principles of management after due deliberation.
Fayol’s Principles of Management
These principles are listed below:
Division of Work
The whole pie of work is divided into several pieces to grab them easily. A trained specialist who is competent to perform a particular aspect of work is assigned the same and it ultimately leads to specialisation. Goals can be accomplished more efficiently if the work is divided into specialised tasks, each performed by a trained employee. This proves the reason behind existence of different departments in an organisation such as marketing, sales, production, human resource management etc. This principle is pervasive and can be observed at schools, non- profit organizations, household etc.
Authority and Responsibility
Authority is the right to give orders to subordinates and obtain obedience from their in their work. There are two types of authority are official authority , which is authority to command, and personal authority , which is authority of the individual manager. Authority is both formal and informal. Responsibility is corollary of authority. Responsibility is the state of being answerable, and accountable for some tasks done by a person.
Managers require that authority and responsibility commensurate with each other. There should exist proper balance between authority and reponsibility. There should be delegation of enough authority to the employees , but for reasonable performance, authority should be assisted with accountability of the tasks conducted by them.
Discipline
Discipline is the obedience to organisational rules, regulations and employment agreement which are necessary for the working of an organisation. There is need for patient superiors at all levels, so that they can guide other employees at the right time along with strict action to be taken, if required. Here, discipline when applied would mean that the workers and management both honours their commitments and fulfill their tasks with utmost dedication without any prejudice towards one another.

Unity of Command
According to Fayol, there should be one and only one superior for every individual subordinate. If an employee gets orders from two superiors ,there might exist some ambiguity for action to be taken by the employee. If he gets order from one superior and is responsible to him only, the work performance report will be made in a better way. He said that if this principle is violated, “authority is undermined, discipline is in jeopardy, order disturbed and stability threatened”. Dual subordination should be avoided. This will also ensure coordination among various departments.
Fayol Principle In Hindi Translation
Unity of Direction
All the units of an organization should move towards the same objective through coordinated and dedicated efforts. Each group of activities having the same objective must have one head as well as one plan. This ensures unity of action and coordination. It prevents overlapping of activities.
Planetbase is not available for Mac but there are some alternatives that runs on macOS with similar functionality. The most popular Mac alternative is Dwarf Fortress, which is free.If that doesn't suit you, our users have ranked 19 alternatives to Planetbase and nine of them are available for Mac so hopefully you can find a suitable replacement. Planetbase for mac. Planetbase is a strategy game where you guide a group of space settlers trying to establish an outpost in a remote planet. In the game you play the role of the base architect and manager, telling your colonists where to build the structures they will need to survive.
Subordination of Individual interest to General interest:
The interests of the organisation should be considered superior as compared to individual person’s objective. All the employees come from different background and with different objectives which may sometimes be different from that of the organisation as a whole. In all the situations the interest of the company should supersede the interest of any one individual. This is because larger interests of stakeholders are more important than interest of any one person.
Remuneration of Employees

The payroll and compensation should be fair to both employees and the organisation. The employees should be paid a reasonable remuneration so as to guarantee them a reasonable standard of living. But it should be within the paying capacity of the organisation. This will ensure friendly atmosphere and good relationship between workers and management. Moreover, the working of the company will be smooth.
Centralisation and Decentralisation
Centralisation means concentration of decision making power in few hands.
Decentralisation ,on the other hand means dispersal of this power to more number of subordinates.
Fayol says that there is a need of balance to exist between centralisation and decentralisation. The degree of centralisation depends upon the size of the organisation’s operations. There is a positive relationship between size of the organization and decentralisation generally,i.e. larger the size of the organization, larger the degree of decentralisation. For example, it becomes difficult for a single body to administer the operations to be performed in the entire nation, therefore, it calls for appointment of more individuals and granting them more power may be at state or district levels.
Scalar Chain
The formal chain of communication which connects people from high ranks to people from lower ranks is known as scalar chain. This scalar chain should be followed in an organisation so as to establish perfect reporting relationships. This way of connecting superiors to subordinates ensure proper chain of command. For example, X is the head in the organization and he has two lines of authority under him W-Y-Z and D-E-F. If, let’s say, Y has to communicate to E, he has to follow the chain Y-W-X-D-E. This may sometimes lead to distortion of information from one person to another and may also result the process to be delayed. Therefore, a modification named Gang Plank is introduced to cope up in an emergency wherein managers at same level can connect to each other directly without following the long chain of communication. This enables the managers to complete their tasks in shorter period of time, especially in case of emergency.
This reduces a lot of time and helps in effective performance. Positive impacts of this principle include clear communication of information, systematic communication in the organization and faster solution.
Fayol Principle In Hindi Language
Order
Henry Fayol Book On Management
The principle of order ensures availability of right person at the right job and right thing at the right place. It is necessary to achieve organizational goals on time and through minimum cost. Maintenance of order will avoid delay in any of the activities performed by the organisation. If there is a place fixed for each and everything and every person, then there will be no obstacles in the way. For example, if a teacher in school os expected to be in staff room in her free periods, then it makes no sense for a student searching for her somewhere else. If she is available where she is expected, the student can solve his query, but if she is not present in her place then the student might face problem and has to carry his doubt for a longer time.
Equity
Equity refers to treating all the personnel from different background, culture, religion, sex, caste etc. equally. There should be no discrimination among employees relating to their personality or character. All employees should be dealt with utmost fair treatment. This can be observed in multinational corporations working with a large number of employees cultivating various diversities. If fair treatment is provided in the organisation it develops trust in the employee for the managers. Thus, in return organisation will also be benefitted as more devotion and loyalty can be expected from teh employees.
Stability of personnel
Employee turnover should be minimized to maintain efficiency and effectiveness in the organization. Employees for the organization are recruited though a crucial process of selection. They should be placed at a particular position for due time and should be provided reasonable time to showcase their performance. Any job insecurity for employees may result in dishonest behaviour of them towards the organisation and would force them to leave the organization. Moreover, it would become a recurring expenditure for the organization to recruit the personnel time and again. So stability of personnel should be maintained in an organisation as it is considered healthy for growth and prosperity of the business.
Initiative
‘Initiative’ means to take the first step for any prescribed tasks with self confidence or through motivation by some superiors. As it is a trait of intelligent persons, it should be inculcated in the employees of the organisation. Management should keep its hands open to welcome the suggestions from the employees. This will enable employees to develop belongingness with the organisation. It will also maintain a cordial and good relations between employees and management. For example, a box where employees can put in their suggestions in form of a chit either anonymously or disclosing their name , and the management can read all the suggestions time to time. This motivates the employees to initiate and take part in programmes conducted by the organisation.
Espirit De Corps
One of most important of Henri Fayol’s 14 administrative principles, esprit de corps is defined as “a feeling of pride and mutual loyalty shared and fostered by the members of a group.”
“Unity is Strength” is the principle which should be practised main the people working for the organisation.
Fayol Principle In Hindi Meaning
It is rightly said, “United we stand, Divided we fall” and can be observed true when all the employees work overtime in order to meet the targets of the month. This benefits both the employees and the organisation as a whole by increasing revenue and thus profits. It is reflected in the progress of large brands who through their work environment and atmosphere have touched the heights of success.
It can be concluded that management principles are widely applicable and have cast a profound impact on management thinking in the current period of time.